What exactly is Bitcoin mining? Can I generate free Bitcoin using my computer? Is it still financially worthwhile to mine Bitcoin today? Let’s dive into these questions about Bitcoin.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin was designed as a decentralized alternative to traditional banking systems. That means it would be able to process transactions between users without a central authority. You instruct the bank to withdraw $50 from your account in a centralized system and transfer the amount to someone else’s account.
Here, all power rests with the bank controlling the ledger that keeps everyone’s balances.
The Idea of Decentralization
So, how exactly do we run this decentralized ledger? How do we empower people to update this ledger and yet stop them from abusing their powers?
The answer to this challenge lies cleverly within the rules of the Bitcoin system, aptly called the protocol.
I like to think about this answer as a game of “Who Wants to Be a Banker?” In a nutshell, anyone who wants to keep Bitcoin’s transaction ledger called the blockchain, can join in.
It just has to guess a random number that, when passed through some equation the system comes up with, solves it. Easy enough, right? Right, well your computer does the guessing.
The better your machine’s performance, the more guesses it can come up with per second, increasing your chances of solving the equation. If you guess correctly, then you are rewarded in Bitcoins for your successful guess, and you get to add the next set of Bitcoin transactions to the blockchain.

The Bitcoin Mining Process
Now, let’s talk in detail about how the mining process works. After your mining computer has made the correct guess, your mining software decides which pending transactions will be included within the next block.
At this point, you have earned the right to temporarily act as a sort of Bitcoin banker, who updates the Bitcoin transaction ledger known as the blockchain. You broadcast the block you created and the solution to the entire network.
Each computer that verifies your solution will update its copy of the Bitcoin ledger in use with the transactions you included in that block.
Blockchain Updating
Since mining depends on making guesses, it involves another miner who has to guess the number for each block. Clearly, although miners with more powerful hardware have higher chances of winning, the nature of probability dictates it’s seldom that the same miner achieves this success in a continuous manner.
After the validation process gets completed, a certain predefined amount of Bitcoins is generated. This can be thought of as an incentive or reward for your effort to solve the mathematical problem. In addition, you earn any transaction fees associated with the transactions you’ve added to your block.
The Twofold Purpose of Mining
It’s called “mining” because it’s literally digging new Bitcoins out of the network. More precisely, though, it’s a by-product of making sure those transactions are valid. So in a sense, the term can be a bit of a mistermed.
The real purpose of mining is to maintain the ledger in a decentralized order. Now that you finally are familiar with Bitcoin mining, you must be all excited and saying to yourself, “Great! Free money!
How do I get started?”
Not so fast—it is not that easy.

The Mechanics of Mining Difficulty
Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, established mining protocols in a way that makes it increasingly difficult to solve the mining math problem as the total mining power of the network rises.
This means that the mining difficulty is dynamically adjusted in relation to the overall computational power present in the network. If more miners enter the ecosystem, solving the problem becomes more challenging; if many miners depart, it becomes simpler. This adjustment is what is referred to as mining difficulty.
Satoshi Nakamoto’s Purpose
You might be wondering why Satoshi implemented this system. The goal was to ensure a consistent influx of new Bitcoins into the network, which helps to mitigate inflation. The mining difficulty is calibrated so that, on average, a new block is added to the blockchain every 10 minutes.
Keep in mind that this is an average figure; it’s possible to add several blocks in rapid succession, followed by a longer wait for the next one. Over time, however, the average will tend to stabilize at the 10-minute mark.
The Evolution of Mining Power
This self-regulating mechanism has led to a sort of “arms race” among miners seeking the most efficient and powerful mining equipment. In the early days of Bitcoin, the number of miners was relatively small.
Satoshi and his associate Hal Finney were among the few individuals mining Bitcoin on their personal computers. Back in 2009, using just a CPU—your computer’s central processing unit—was sufficient to mine Bitcoin due to the low mining difficulty at that time.

Evolution of Mining Technology
With the popularity of Bitcoin, enthusiasts began to look for stronger methods of mining. This brought about GPU mining. A GPU is a Graphics Processing Unit, which is basically an electronic component dedicated to handling complex mathematical calculations; it was initially developed to enable high-performance gaming.
Their architecture made them favourite components in cryptographic applications, and by 2011, they were in wide usage for Bitcoin mining. Just for perspective, one GPU is equivalent in mining performance to about 30 CPUs.
Switching to FPGA Mining
The next big hardware development breakthrough was FPGA mining. A Field-Programmable Gate Array, or FPGA, is a type of hardware attached to a computer to conduct specific types of calculations.
Thus, while FPGAs can power processing speeds 3-100 times faster than a GPU, the configuration of an FPGA is much more challenging, making it less popular among miners.
ASIC Bitcoin Miners
2013 saw the development of ASIC miners. ASIC stands for Application-Specific Integrated Circuit. Such devices were designed only to mine Bitcoins. Unlike GPUs, CPUs, and FPGAs, ASICs cannot be used for performing other tasks because their work is hardwired into hardware.
ASIC miners have become a standard today in mining. Some early ASIC miners were available as USB devices, but they became outdated soon. Although ASIC technology was introduced in 2013, it developed very fast with more powerful versions coming into the market about every six months.
After three years of hectic technological development, things have normalized and the race to introduce new miners has significantly receded compared to 2016.
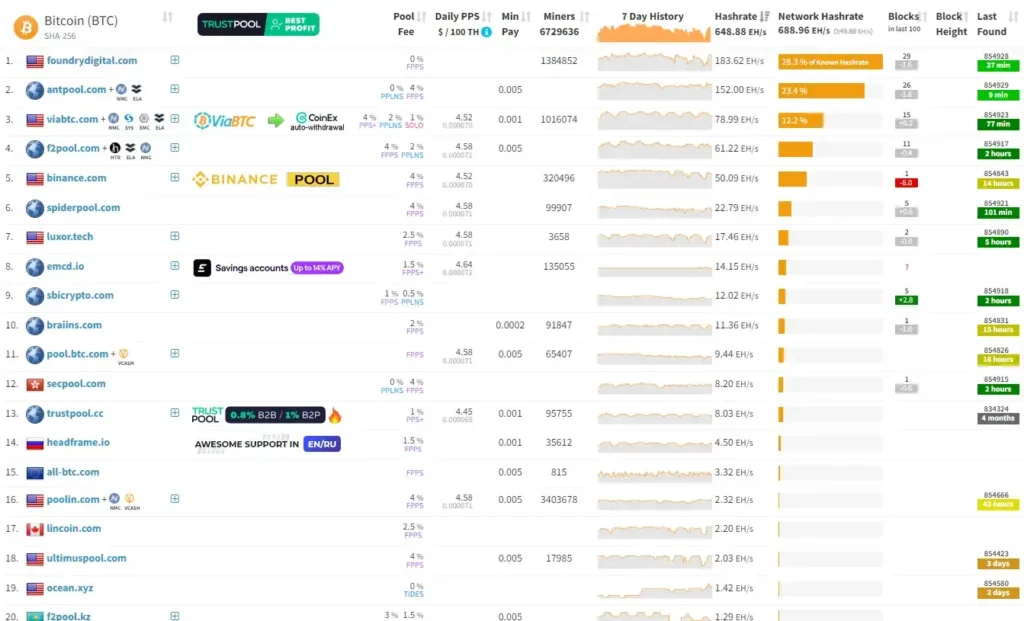
The Role of Mining Pools
Now that we know what miners are, let us discuss mining pools. For new entrants into the Bitcoin mining space, competition is very high. Even if you get the best available mining equipment, you are still far outgunned by professional mining farms.
It was this problem that led to the development of mining pools.
Collaborating for Success
The concept is simple: miners band together to create a “pool,” pooling mining power to increase their competitiveness. If the pool mines a block, the rewards are then divided among members according to each person’s contribution of mining power.
In such a way, smaller miners can still compete and earn Bitcoin, although at a much smaller proportion of the total reward. To this day, more than a dozen significant mining pools compete with each other in mining the precious, so-called Bitcoin, along with updating a blockchain ledger.
Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable?
By now, you should be probably wondering, “This all sounds great, but is Bitcoin mining actually profitable in today’s market?”
The short answer would be “probably not,” while the longer one, more accurate, would be “it depends on various factors.”
Several elements influence the profitability of Bitcoin mining, so let’s look into them briefly.
Factors Influencing Profitability
A hash refers to the mathematical problem being solved by a miner’s computer. The Hash Rate, therefore, is normally a measure of the performance of your mining equipment: it shows how many guesses it can produce per second.
It can be measured in mega hash per second, giga hash per second, terra hash per second, and even peta hash per second. The block reward was halved from the original 50 Bitcoins back in 2009, and so it shall continue to decrease every 210,000 blocks, for approximately four years. As of August 2024, the latest halving event, which happened this April 2024, puts the miner’s remuneration at 3.125 BTC per block.

Another would be the mining difficulty, which is a measure of how hard it is to mine Bitcoins at any point in time, as visible by the total mining power active on the network. You’ll also need to know your electricity cost in dollars per kilowatt-hour.
Mining involves huge amounts of energy to run equipment and cool it down, as mining rigs may generate quite a lot of heat. Every mining setup comes with a different consumption of power usually measured in watts. Knowing the exact energy requirements of your miner is important in finding out its profitability.
Also, if you mine through a pool—which is highly recommended—a percent of your rewards will go to the pool for their services. Also, since Bitcoin’s future price remains unknown, it can have a huge impact on your overall profitability, especially if you plan to convert your mined Bitcoins into another currency at some point down the road.
Understanding Mining Difficulty Changes
Finally, mining difficulty change is perhaps the biggest variable and the one which is least predictable. As the influx of miners ebbs and flows, nobody really knows how much harder mining will become in the near future—weeks or even years from now.
Bitcoin’s profitability has historically dropped a few times, but the cryptocurrency was lower-priced. The unpredictability of the last two factors makes it pretty impossible to provide a crystal-clear answer to the question, “Is Bitcoin mining profitable?”
To get a better approximation of the possible earnings, gather these variables and enter them into a Bitcoin mining calculator. If you get a negative number from it, that would mean that your mining conditions aren’t that suitable for profitability at that time.

Alternative Mining Approaches
By now, you probably have a sense that mining is the right choice for you. But, you also might have stumbled upon other mining methods that include cloud mining, mobile mining, or web mining.
Cloud Mining
In cloud mining, you can rent computing resources from a mining company rather than invest in your personal mining rig. You then get paid based on the amount of mining power you hire. This may sound pretty good because it dispels all the hassle of buying, hosting, cooling, and managing mining equipment.
However, a closer inspection of most cloud mining services turns out to be poorly serving investment opportunities. Those that do turn out to be profit-oriented may turn out to be scams executed as complex Ponzi schemes that don’t own any actual mining equipment. The general rule of thumb is to avoid cloud mining.
If you do, ensure you do detailed calculations before you invest your money into it.
Mobile Mining
Some mobile apps claim to mine Bitcoin directly off your smartphone. Technically, it’s possible, but due to the very limited processing powers of the mobile phone compared to the ASIC miner, you will more than likely be draining your phone’s battery considerably faster and will end up receiving a very minimal fraction of one Bitcoin.
These apps pool the resources of various mobile users and then reward them accordingly, based on their computational contribution to that process. Yes, you can mine with any ordinary computer; keep in mind that the energy it consumes almost always outweighs any potential rewards—you could do it, but with very low chances of significant return on investment using slower machines.
Web Mining
The term web mining is a quite recent concept, dating back to 2017, by which the operators of a website can make use of their visitors’ CPUs to mine Bitcoin. Said another way, thousands of unknowing users’ computers can be used to create an income stream for the site owners.
Given that, in most instances, it is not profitable to mine Bitcoin with a CPU, a lot of websites using web mining alternate between mining other cryptocurrencies. As it is pointed out by the last measurements, more than 20000 sites have already embedded web mining. The method is extremely controversial. From the visitors’ point of view, the impression is that their machines are used without consent.
The visitors blame web mining for overheating the visitors’ computers and damaging their CPUs. From a website owner’s perspective, web mining offers an innovative way of generating money, without having to resort to intrusive ads, while allowing the website owner to control how much visitor’s CPU power is used to prevent overload on their hardware.

Common Questions About Bitcoin Mining
Finally, here are three commonly asked questions that I thought would be worth addressing:
Is Bitcoin Mining a Waste?
There has been quite a lot of fuss over the amount of energy used by Bitcoin miners worldwide; however, there are a couple of counterpoints worth mentioning.
First, one might argue that Bitcoin mining actually uses fewer resources than our current banking infrastructure does. If one were to consider the consumption by banks, servers, ATMs, credit card companies, and all other components that make up this traditional financial system, what can be logically derived is the fact that this system is far less efficient than Bitcoin mining.
Not to speak of the natural environment that the physical currency production process affects, such as paper production and pollution created by these institutions. Moreover, Bitcoin mining may serve to increase the utilization of energy more efficiently globally.
Most mining companies are moving to countries with a supply of excess electricity. These are only some of the points that validate Bitcoin mining.
Can Big Companies Replace Individual Miners?
People often ask, “Wouldn’t a company like Google just get into the Bitcoin mining business and dominate the field?
Technically, yes, it could, but doing so would not give a tremendous advantage. The reason is that Google’s servers aren’t designed to perform the Bitcoin mining problem as easily as ASIC miners do.
If Google were to dedicate all its servers solely to Bitcoin mining and turn off everything else, that would equate to only about one-thousandth of a percent of the current mining power on the Bitcoin network.
Should You Mine Bitcoins?
Finally, “Is Bitcoin mining something for me? ”
By now, after reading this guide, you should have a pretty good idea. It’s important to remember that, depending on market conditions, there could well be more profitable alternatives to Bitcoin mining.

For instance, during those wild swings in value, you may be better off just buying Bitcoins instead of trying to mine them. Alternatively, you could mine altcoins that are still viable using just a GPU, such as Ethereum, Monero, or Zcash.
Conclusion
Above, we have tried to explain with clarity the process involved in updating Bitcoin’s ledger of transactions: incentivized by rewarding participants with new Bitcoins.




Recent Comments